SOCKS5 proxies in simple terms: how they work and where they are used
30.12.2025Imagine this: you’re sitting in a café with poor Wi-Fi, trying to watch a TV series, but the service says “content is not available in your country.” Or you launch a parser, and it keeps getting blocked by IP. These annoying situations are familiar to many people. This is where SOCKS5 comes to the rescue.
A SOCKS5 proxy is one of the simplest yet most powerful tools designed to solve exactly these kinds of problems.
Proxy — is a server through which your network traffic passes. Instead of connecting directly to the target resource, your device establishes a connection with the proxy, and the proxy then connects to the resource and forwards the responses back to you.
What is SOCKS5
SOCKS5 is one of the most versatile types of proxies. Unlike an HTTP proxy, which works exclusively with web requests, SOCKS5 operates at a lower level and simply forwards network connections. It supports both TCP and UDP, making it suitable for a wide range of tasks — from regular browsing to online games, VoIP, and torrents. SOCKS5 does not provide traffic encryption, so if confidentiality is required, it is usually combined with a VPN or tunneling.
How a SOCKS5 proxy works
- Your application (browser, game, torrent client, etc.) establishes a connection to a SOCKS5 proxy over TCP (or UDP if required).
- The application sends requests and data through this connection — the proxy receives them.
- The proxy “masks” your requests (hides your real IP, and if necessary modifies some network fields) and opens a new connection to the target server on the internet.
- The target website or service communicates with the proxy and assumes that the proxy itself is the source of the requests.
- When the website responds, the proxy receives the responses and forwards them back to your application, matching incoming responses with your original requests.
Key features and advantages of SOCKS5
Versatility SOCKS5 is suitable for various tasks and applications because it operates at the socket level and can forward any network traffic — not only web pages (HTTP), but also traffic from games, torrent clients, VoIP, DNS, and more.
Improved connection stability Since SOCKS5 simply redirects TCP/UDP connections, it usually provides more stable behavior for long-lasting or latency-sensitive connections (for example, online games or video calls).
Configuration flexibility SOCKS5 supports authentication (username/password), works with both TCP and UDP, and can be configured either system-wide or only for specific applications. This flexibility allows you to route only certain programs through the proxy without affecting the rest of the traffic.
Where SOCKS5 proxies are used
SOCKS5 is used:
- when you need to change your visible IP and increase anonymity while browsing;
- for torrents and P2P, because it allows UDP traffic and does not interfere with higher-level protocols;
- in online games and VoIP, where stability and proper routing are critical;
- for web scraping and automation, to distribute requests across different IPs;
- in corporate networks for traffic control and logging;
- in combination with SSH or VPN to create more flexible tunnels.
SOCKS5 vs other types of proxies
By protocols
- SOCKS5 supports almost any protocol over TCP and UDP, allowing it to proxy web traffic, torrents, games, VoIP, and more.
- HTTP proxies are focused on HTTP/HTTPS and are not suitable for directly proxying most other protocols without additional workarounds.
By encryption
- SOCKS5 itself does not encrypt traffic — it simply forwards packets.
- HTTPS proxies usually imply TLS protection of the channel between the client and the proxy (while HTTPS sessions between the client and the website are encrypted independently).
By data processing
- An HTTP proxy interprets and can modify HTTP headers, cache responses, and filter content.
- SOCKS5 does not analyze or modify content — it only forwards connections and maps responses back to the client.
Compatibility and use cases
- SOCKS5 is suitable for applications that support SOCKS (many desktop applications, torrent clients, games).
- HTTP proxies are convenient for browsers and services that specifically work with HTTP/HTTPS and benefit from HTTP-level features (cache, filters, header-based authentication).
Ports and firewall bypassing
- The classic SOCKS port is 1080.
- HTTP proxies more often listen on ports 80, 8080, 3128, etc., while HTTPS proxies usually use port 443 for encrypted access. To bypass network restrictions, it can sometimes be easier to “disguise” traffic through HTTP/HTTPS ports, since these ports are often open in corporate networks.
Authentication and configuration
- SOCKS5 supports simple authentication (for example, username/password).
- HTTP proxies can also require authorization and additionally enforce policies and logging at the HTTP level.
Setting up and testing SOCKS5
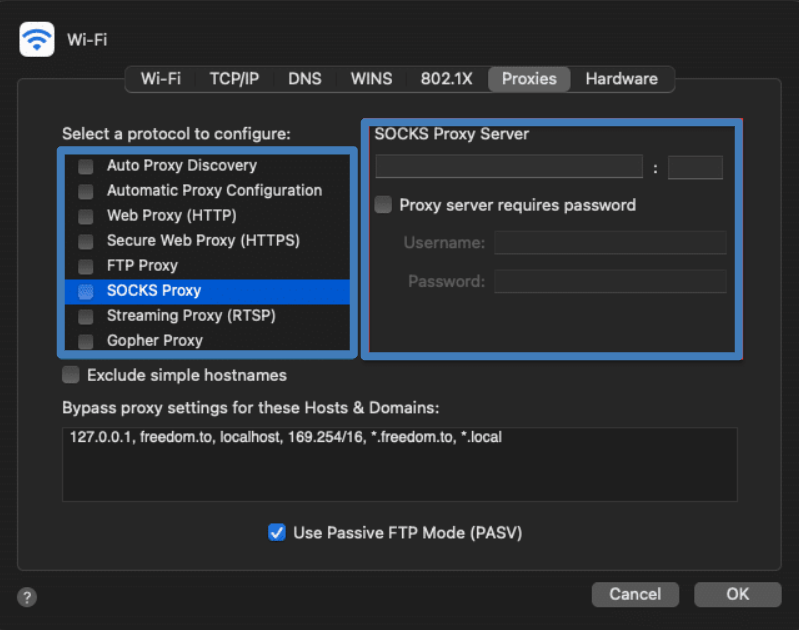
macOS
- Open System Settings and go to the “Network” section.
- Select the network interface you use to access the internet (Wi-Fi or Ethernet), click “Advanced,” and switch to the “Proxies” tab.
- Check the box next to “SOCKS Proxy” (or “SOCKS5”), enter the proxy server address and port (usually 1080), and specify a username and password if required.
- Click OK and apply the changes. Then restart your browser or other application so it starts working through the proxy.
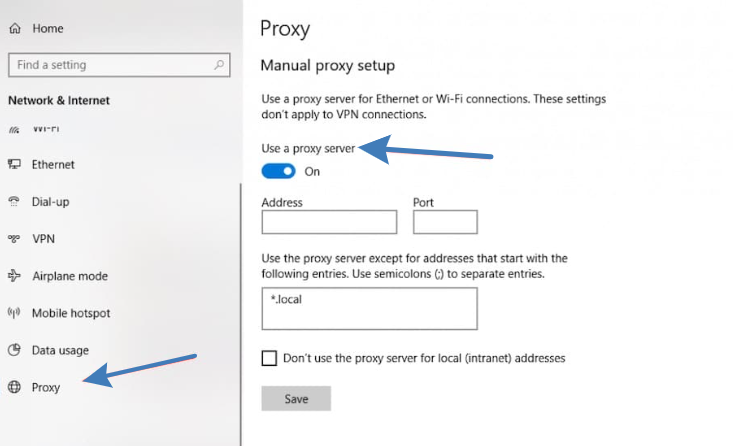
Windows (two methods)
Via the Settings menu:
- Open “Settings” → “Network & Internet” → “Proxy.”
- In the manual proxy setup section, you can enable the configuration and specify the address and port.
- Note: the standard Windows Settings interface is more oriented toward HTTP/HTTPS proxies rather than SOCKS explicitly, so this method may not work for all applications.
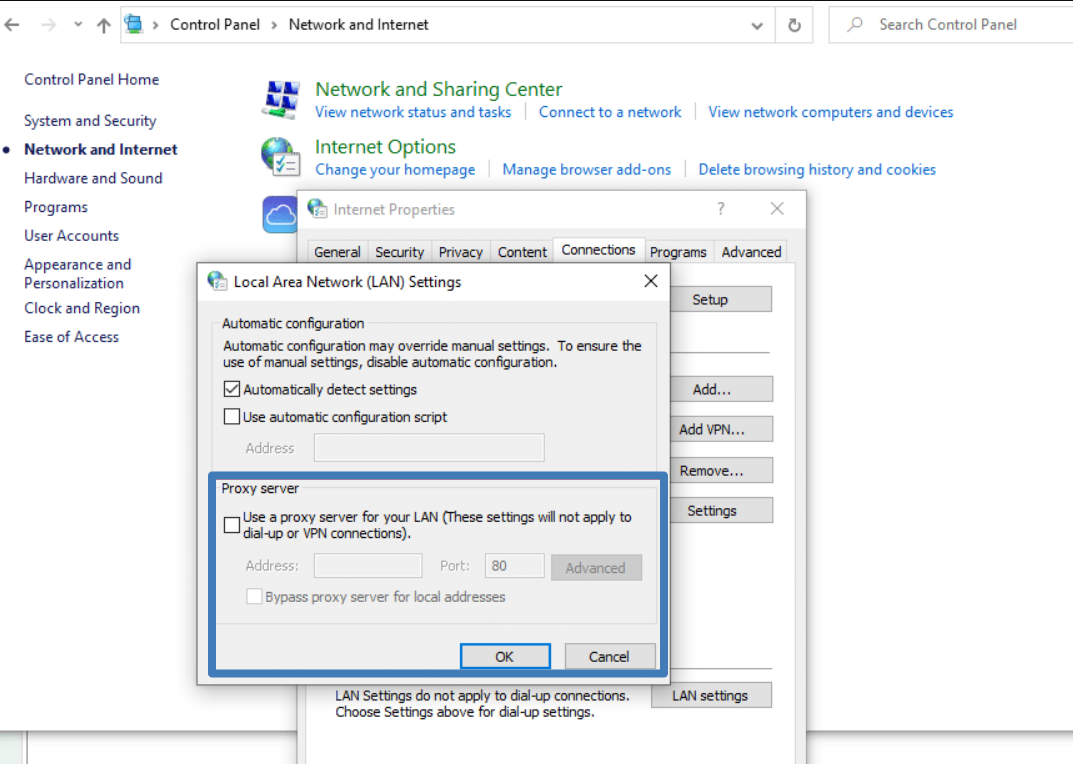
Via the classic Control Panel:
- Open Control Panel → “Network and Internet” → “Internet Options.”
- Go to the “Connections” tab, click “LAN settings,” then “Advanced.”
- In the “Proxy Server” window, there is a field for SOCKS — enter the proxy address and port there, confirm, and save.
- After that, applications that use system proxy settings will start working through the SOCKS server (restart the applications).
How to choose a proxy service
Criteria for choosing a proxy service
- Evaluate the service based on real technical characteristics and ease of management.
- First of all, pay attention to connection stability and speed. What matters is not what is promised in the description, but how the proxies perform under load.
- Consider the types of IPs (residential or datacenter), geographic coverage, and supported protocols (SOCKS5, HTTP/HTTPS), as these determine compatibility with your applications.
- Check the logging and security policy: whether logs are stored, how authentication is handled, and whether channel encryption is available. IP rotation, session management, a convenient dashboard or API for automation, and good documentation are also useful features.
What Belurk offers
The Belurk service provides reliable proxies for a wide range of tasks — from browsing and parsing to working with P2P and gaming traffic. Different IP types and geolocations are available, popular protocols are supported, and tools for managing and monitoring proxy performance are provided. Belurk focuses on connection stability and responsive technical support, allowing you to quickly set up proxies and start working. If needed, the team will help you choose the optimal proxy type for your specific requirements.
Try belurk proxy right now
Buy proxies at competitive prices
Buy a proxy